Chinese Big Tech ‘Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.’ selling smart gadgets and ICT (Information and Communications Technology) infrastructure, is the talk of the business world lately. Ever since its inception in Shenzhen, China, in 1987, Huawei has grown to operate in more than 170 nations, manufacturing communications devices, providing devices & services, and constructing telecom networks. With over 207,000 workers, Huawei provides services to over three billion people globally.
What is the hype about Huawei’s latest earnings ‘doubled 2023 Profit’?
Huawei Technologies, a Chinese tech company, announced on Friday that its net profit for 2023 more than doubled, with revenue increasing year over year across all business segments. Huawei recorded its largest net profit in the previous five years, adding up 87 billion yuan (USD 12 billion), with the exception of 2021, when it realized an undisclosed gain from the spinoff of its low-cost smartphone brand, Honor.
The figures are a clear indication that the business has survived Washington’s prolonged campaign, which has included strict export regulations. Especially in the home smartphone market, Huawei’s comeback has forced pressure on competitors, most notably Apple.
Formerly the second-largest smartphone manufacturer in the world, Huawei reported that sales of its consumer electronics division, which is affected by sanctions, increased 17.3% from 2022 to 251.5 billion yuan in revenue last year, and that growth is anticipated to continue into the 1st quarter in 2024.
Moreover, Huawei reported that the number of devices using its Harmony OS has increased to over 800 million across all platforms, from roughly 330 million at this time last year. Once Washington shut off the company’s access to American technologies, it turned its attention to creating a rival operating system to Google’s Android OS. In contrast, BusinessofApps estimates that there are approximately 3.9 billion active smartphones implemented with Android OS, making it the most popular OS worldwide.
Following the release of its leading Mate 60 Pro series smartphone in the previous year, Huawei had a successful year. The company managed to incorporate cutting-edge 7-nanometer IC (integrated circuit) technology in the premium model even though U.S. export regulations prevent it from doing business with leading international chipmakers. Washington is considering strengthening export regulations even more as Huawei’s success is perceived as a Chinese win over the United States in the tech race. For the majority of its handsets, Huawei still gets its 4G mobile CPUs from American semiconductor manufacturer Qualcomm.
Huawei Focuses on Making AI Processors

According to reports, Huawei is now refocusing its chip technology efforts to make AI processors while decreasing the output of the chips required to power smartphones. According to a statement released by Huawei, its rotating chairman Ken Hu said that they had experienced difficult stages over the past few years, but despite facing numerous obstacles, they have succeeded in developing.
It became difficult for Chinese computer companies to acquire the chips they required for AI creation due to U.S. limitations on advanced technology imports to China from U.S. tech companies, the most recent of which was imposed in October. There is also a simmering chip war. Huawei is being forced to turn inward due to the impact of US export restrictions; as per The Journal, nearly 70% of the company’s income received from the Chinese clients in the previous year.
Huawei’s Profit Pressurizing Other Market Vendors
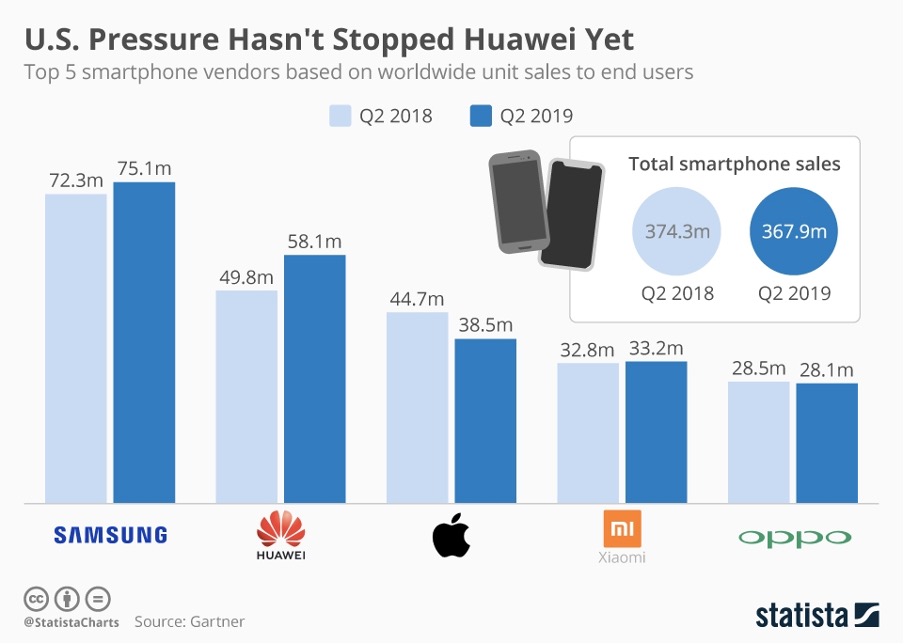
Reportedly, Huawei recovered well in China during the 2nd half of 2023, moving back into the top five. Analysts claim that it continued to gain significant traction until the first few months of 2024. However, given China’s already extremely competitive market, this comeback is placing pressure on other vendors. In 2023, China accounted for 94% of Huawei’s smartphone shipments.
Apple is most definitely feeling the heat from Huawei’s comeback. In an effort to strengthen its position in the market, Apple has recently boosted its investments in China. These include large expenditures on co-marketing campaigns, the opening of a new Apple shop, and Tim Cook’s (CEO) visit, according to reports.
Ken Hu, Huawei’s rotating chairman, stated on Friday that the company’s total performance in 2023 was consistent with projections and that it had grown in spite of several challenges one after another.
The company’s revenue increased 9.6% to 704.2 billion yuan for the entire year 2023 from 642.33 Bn yuan in 2022. Its R&D expenditures reached a new all-time high of 164.7 Bn yuan, or around 23.4% of its overall sales. Over the last ten years, it invested 1.11 trillion yuan in R&D.
The rapidly increasing demand for generative Artificial Intelligence technology led to significant development in the company’s cloud business. In 2023, the unit’s revenue increased by 21.9% year over year to 55.3 Bn yuan. Users of Huawei’s Pangu training model include the (ECMWF) European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts and iFlytek, China’s speech recognition AI champion.
Huawei’s ICT infrastructure division, which comprises its enterprise and carrier businesses, continued to be the company’s main source of income with sales increasing 2.3% to 362 billion yuan.
Huawei, which ranked as the top global provider of telecom equipment in 2023, began implementing 5.5G wireless network technologies both domestically and internationally, notably in Brazil, Turkey, and the Middle East. According to Huawei, certain telecom providers in Germany and Finland also finished the technology’s verification, an essential step before using it.
Sales of the company’s fledgling automotive electronics division more than doubled to 4.7 billion yuan in 2022. Although it solely caters to the domestic market, it has partnerships with several Chinese automakers, including Seres and Baic Group.

